 Researchers from the University of Tokyo treated the surfaces of nanoparticles with polymers and enabled the transport of quantum dots into cells, according to a study published in Science and Technology of Advanced Materials.
Researchers from the University of Tokyo treated the surfaces of nanoparticles with polymers and enabled the transport of quantum dots into cells, according to a study published in Science and Technology of Advanced Materials.
By coating nanoparticles with MPC polymers, researchers can make substances that are easily transported and delivered into the blood or other tissue because the polymer mimics cellular membranes. Nanoparticles treated with MPC polymers can be used as anti-tumor compounds, gene carriers, and contrast agents to improve MRI images, according to the study.
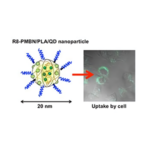
Researchers at the University of Tokyo used the polymeric nanoparticles to transport quantum dots, a nanoparticle made of semiconducting material, into cells. Using a solvent-evaporation technique, the team was able to create polymeric nanoparticles with a core of quantum dots. The particles can outperform conventional organic fluorescent dyes in biomedical imaging, according to the team. The particles maintained the same levels of fluoresence in solution after being stored for more than six months at 4 °C and in environments of varying acidity.
Conventional dyes lose their fluorescence over time with repeated illumination, but the polymeric nanoparticles filled with quantum dots did not.
The team also showed that when they attached a cell-penetrating peptide called R8 to the polymeric nanoparticles, the particles were taken up by the cells within 5 hours and had no inflammatory effect on the cells after several days. The
“This was the first report showing the long-term retention of nanoparticles in cells,” lead researcher Kazuhiko Ishihara said in prepared remarks. “Preparation of bioactive nanoparticles with MPC polymers can be used to fabricate in-cell nanodevices whose interaction with cells can be completely controlled.”
