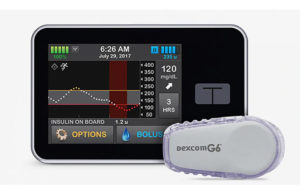
The study demonstrated improved blood sugar control in children ages 2-6 with type 1 diabetes. It evaluated an artificial pancreas using the Tandem t:slim x2 insulin pump with Control-IQ technology. Results were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Tandem’s Control-IQ technology automatically monitors and regulates blood glucose. The artificial pancreas utilizes an insulin pump with advanced algorithms based on glucose monitoring from the Dexcom G6 CGM. Then it adjusts the insulin dose as needed. Control-IQ has FDA clearance for people ages six and older with type 1 diabetes.
Findings from the study included participants spending approximately three more hours per day in their target blood sugar range with the artificial pancreas. This compared to a control group of participants who continued relying on their existing methods for managing blood sugar.
“After the resounding success of Control-IQ technology in people ages 6 and up, it is very rewarding to see our youngest patients, and often the most challenging patients to help, benefit as well,” said Marc D. Breton, a UVA School of Medicine researcher who served as the trial’s principal investigator. “With these results, we have now accumulated years of clinical validation of this system across all age groups and look forward to seeing this life-changing technology made available to the broadest possible population.”
Tandem tech proves effectiveness for young kids in study
The study enrolled 102 children between two and six years old across three U.S. sites (UVA, Stanford University and the University of Colorado). It randomly assigned 68 to use the artificial pancreas for 13 weeks while the remaining 34 children represented the control group. All participants maintained regular daily routines during the 13-week study.
On average, participants in the artificial pancreas group spent 12.4% more time within their target blood glucose range compared to the control group. They also spent 18% more time in range during overnight hours (10 p.m. to 6 a.m.).
The researchers say the participants were overall able to use the artificial pancreas safely. They reported two cases of severe hypoglycemia in the artificial pancreas compared with one in the control. One case of diabetic ketoacidosis also occurred in the artificial pancreas group. A failure of the thin plastic tube that connects the insulin pump to the patient’s body caused this.
Most study-related visits (including 80% of training sessions and 90% of overall sessions) operated virtually. The researchers say this highlights the potential of the technology in areas without easy access to endocrinologists.
“At the end of the day, this technology significantly improved glycemia and ensured safety of our youngest patients, but perhaps just as importantly it lessened these families’ constant anxiety about glucose levels, especially during the night.” Breton said. “It is incredibly rewarding for us to hear about these families’ experiences and how they manage to integrate these new tools in their life, offering some reprieve to the challenges they face.”
More data highlighted from the study
The percentage jumps for time in range brought Control-IQ users to 69%, compared to 56% in the control. HbA1c decreased 0.5% from baseline with the artificial pancreas, marking a median improvement of 0.42% compared to the control.
Control-IQ users spent 5.4% less time in hyperglycemia compared to control. Hypoglycemia rates were low but not statistically different between groups. Tandem said Control-IQ results registered immediately (evident within one day of initiation) and were sustained.
The nighttime time in range came in at 74% with Control-IQ compared to 56% in the control group. Daytime was 67% to 56%, respectively. Both groups demonstrated similar total daily insulin dose and weight change.
According to Tandem, the median time the system was in active closed loop was 94%. Results were observed regardless of pre-study experience with an insulin pump. All but one patient completed the 13-week trial.
“Use of the t:slim X2 insulin pump with Control-IQ technology demonstrated substantial improvements in glucose control, particularly overnight, with no increase in hypoglycemia in young children,” said Dr. Jordan Pinsker, VP and medical director at Tandem Diabetes Care. “Initiating pump therapy with automated insulin delivery can be very daunting for parents. A system offering these clinical benefits that is simple enough to start with virtual training makes the t:slim X2 insulin pump an excellent therapeutic option for this population.”
The National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, funded the study. Tandem Diabetes Care provided the investigational closed-loop systems used in the trial, while Dexcom provided the CGM.

